Living Beings and Their Structure | Chapter 3 | Grade-7 | Science and Technology Notes - New Course 2079-2081
3.1 Different Types of Organisms.
Test Your Concept
1. Match the following.
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| reproductive organ | maize |
| fibrous root | flower |
| reticulate venation | anther |
| stamen | bean |
| fertilization | transfer of pollen grains |
| pollination | fusion of gametes |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| reproductive organ | flower |
| fibrous root | maize |
| reticulate venation | bean |
| stamen | anther |
| fertilization | fusion of gametes |
| pollination | transfer of pollen grains |
2. Multiple choice questions (MCQs):
a. Which of the following is the food factory of a plant?
A) root
B) shoot
C) leaf
D) stem
Answer: C) leaf
b. Which of the following makes flowers attractive?
A) sepal
B) petal
C) leaf
D) cotyledon
Answer: B) petal
c. Which of the following protects the flower in the bud state?
A) sepal
B) petal
C) leaf
D) stem
Answer: A) sepal
d. Which of the following is the root?
A) potato
B) sweet potato
C) ginger
D) garlic
Answer: B) sweet potato
e. Which of the following bears a complete flower?
A) mustard
B) maize
C) pumpkin
D) cucumber
Answer: A) mustard
Also Check:
Energy In Daily Life | Chapter 7 | Grade-7 | Science and Technology Notes - New Course 2079-2081
Information and Communication | Chapter 2 | Grade-7 | Science and Technology Notes - New Course 2079-2081
Scientific Studies | Chapter 1 | Grade-7 | Science and Technology Notes - New Course 2079-2081
3. Differentiate between:
a. stem and root
Answer: The differences between stem and root are -
| Stem | Root |
|---|---|
| 1. Stem develops from plumule. | 1. Root develops from radicle. |
| 2. Stem is the plant structures bearing shoots and buds with leaves. | 2. Root is the part of the vascular plant that is underground typically. |
| 3. Stem is the aerial part of the plant body. | 3. Root is the underground part of the plant body. |
| 4. Stem moves away from water. | 4. Root moves towards water. |
| 5. Stem grows against the force of gravity. | 5. Root grows towards the force of gravity. |
| 6. Stem is generally green in colour. | 6. Roots is generally colourless. |
| 7. Stem is with nodes and internodes. | 7. Root is without nodes and internodes. |
| 8. Stem bears leaf, bud, flower and fruit. | 8. Root does not bear leaf, bud, flower and fruit. |
| 9. Branches develop near the tip. | 9. Branches develop behind the tip. |
| 10. Stem hair are multicellular and they are of various sizes and shapes. | 10. Root hair is unicellular and they are tube like. |
| 11. Stem stores very little food. | 11. Root store excess food. |
| 12. Stem absorbs carbon dioxide gas and oxygen through the stomata present on leaf surfaces. | 12. Root absorbs water and mineral nutrients from the soil with the help of root hairs. |
b. root system and shoot system
Answer: The differences between root system and shoot system are -
| Root System | Shoot System |
|---|---|
| 1. Root System is the part of the plants that grows into the ground. | 1. Shoot System is the part of the plants that grows above the ground. |
| 2. The important functions of root system are absorbing water and minerals from the ground, and providing support to the plant on the ground. | 2. The important functions of shoot system are Photosynthesis, transport of materials, and reproductions. |
| 3. Root system is composed of roots, tubers and rhizomes. | 3. Shoot system is composed leaves, buds, flowers and fruits. |
| 4. Root system does not go under photosynthesis. | 4. Shoot system undergoes photosynthesis. |
| 5. Root system does not undergo se*ual reproduction. | 5. Shoot system undergoes se*ual reproduction by means of flowers. |
| 6. Root system cannot be used as timber. | 6. Shoot system can be used as timer. |
c. pollination and fertilization
Answer: The differences between pollination and fertilization are -
| Pollination | Fertilization |
|---|---|
| 1. Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from an anther to a stigma of a flower. | 1. Fertilization is the fusion of haploid male and female gametes forming the diploid zygote. |
| 2. Pollination is a physical process. | 2. Fertilization is a biochemical, genomic, and cellular process. |
| 3. Pollination is an external process. | 3. Fertilization can either be internal or external. |
| 4. Pollination agents are wind, water, birds, insects, and other animals. | 4. Fertilization takes place by growing pollen tube which enters the ovule. |
| 5. Pollination process leads to fertilization. | 5. Fertilization process leads to the formation of seeds. |
| 6. In pollination process, the pollen tube is not required. | 6. In fertilization process, pollen tubes are formed for transferring male gametes into an egg cell. |
| 7. Pollination occurs in flowering plants only. | 7. Fertilization occurs in almost every plant and living being. |
d. stamen and pistil
Answer: The differences between stamen and pistil are -
| Stamen | Pistil |
|---|---|
| 1. Stamen is the male reporductive organ of the flower. | 1. Pistil is the female reproductive organ of the flower. |
| 2. Androecium is the other name for stamen. | 2. Gynoecium is the other name for pistil. |
| 3. Stamen produces pollen grains. | 3. Pistil mainly produces ovules. |
| 4. Stamen contains total two parts and are anther and filament. | 4. Pistil contains total three parts and are stigma, style and ovary. |
| 5. Stamen is mainly found outside the pistil and pollen grains are produced by the stamen. | 5. Pistil is mainly found at the centre of the flower and it bears number of ovules in the ovary. |
| 6. During pollination, pollen grains release to the environment. | 6. Stigma of pistil captures pollen grains. |
4. Give reasons:
a. The flower of pumpkin is incomplete.
Answer: The flower of pumpkin is incomplete because pumpkin has only three fundamental floral parts, i.e. calyx, corolla and androecium or gynoecium.
Or,
The flower of pumpkin is incomplete because pumpkin has only one reproductive part, which could be male (stamen) or female (pistil), but not both reproductive parts together.
Or,
Pumpkin is not a complete flower because neither the male nor the female reproductive parts are present in a single flower of pumpkin.
The examples of incomplete flowers (plants) are as follows:-
1. Bittergourd.
2. Squash Plant.
3. Pumpkin.
4. Sweetcorn.
5. American holly tree.
6. Papaya.
7. Watermelon.
8. Cucumber.
9. Begonia.
10. Oaks.
11. Bottleguard.
12. Sunflower lay florets.
13. Marigold.
14. Sweet Pea.
15. Cassava.
16. Date palm.
17. Mulberry.
18. Jatropha.
19. Anemone.
20. Cottonwood flower.
b. The flower of hibiscus is complete.
Answer: The flower of hibiscus is complete because hibiscus has all four fundamental floral parts, i.e. calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium.
Or,
The flower of hibiscus is complete because hibiscus has both male (stamen) and female (pistil) reproductive structures.
Or,
Hibiscus is a complete flower because hibiscus bear all four parts - sepals, petals, stamens and pistils.
The examples of complete flowers (plants) are as follows:-
1. Lily.
2. Rose.
3. Sunflower.
4. Tulip.
5. Daffodil.
6. Mustard.
7. Brinjal.
8. Hibiscus.
9. Tomato.
10. Long bean.
11. Chilli.
12. Country bean.
13. Mango.
14. Sweet Peas.
15. Gulmohars.
16. Trumpet Vine.
17. Pea.
18. Lemon.
19. Guava.
20. Curry Tree.
c. The root of garlic is fibrous.
Answer: The root of garlic is fibrous because garlic does not have primary, secondary and tertiary root.
Or,
The root of garlic is fibrous because garlic doesn't have any root hairs, root tips and root cap.
Examples of some plants with Fibrous Roots are -
(1) Banyan Tree.
(2) Sugarcane.
(3) Sweet Potato.
(4) Asparagus.
(5) Dahlia.
(6) Screw pine.
(7) Maize.
(8) Grass.
(9) Orchids.
(10). Basella and Portulaca.
(11) Money Plant.
d. The root of chilli is tap.
Answer: The root of chilli is tap root because chilli has primary, secondary and tertiary roots.
Or,
The root of chilli is tap root because chilli has root hairs, root tips and root cap.
e. Leaf is a part of the shoot system.
Answer: Leaf is a part of the shoot system because it is a part of a plant body that grows above the ground.
f. Leaf is the food factory of a plant.
Answer: Leaf is the food factory of a plant because it prepare food by the process of photosynthesis.
Or,
Leaf is called the food factory of a plant because it makes food by the process of photosynthesis with the help of raw materials like water and carbon-dioxide using sunlight and chlorophyll.
g. Roots modify into different forms.
Answer: Roots modify into different forms because it provides mechanical support to the plants, respirations, stores food, absorbs water and minerals, and also helps in reproduction.
5. Short answer type questions:
a. What are the basic parts of a flower?
Answer: The basic parts of a flower are -
i) Calyx,
ii) Corolla,
iii) Androecium.
iv) Gynoecium.
b. What is a receptacle?
Answer: The swollen tip of the pedicel from which the floral parts grow is called a receptacle.
Or,
Receptacle is a swollen end of the flower stalk where the floral parts of a flower are arranged.
Or,
A receptacle are the vegetative tissues near the end of reproductive stems, situated below or encase the reproductive organs.
c. Define pollination?
Answer: Transformation of pollen grains from the anther (male part) to the stigma (female part) is called pollination.
Or,
The process by which pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of the same or another flower is known as pollination.
Or,
Pollination is the main mode of se*ual reproduction in plants, which occurs when the transfer of pollen grains (male) from the anther of a flower to a stigma (female).
d. Define fertilization?
Answer: The fusion of male and female gametes is called fertilization.
Or,
The process in which the male gametes present in pollen grain fuses (joins) with the female gametes present in ovule to form a new cell called zygote is called fertilization.
e. Write a function of fruit.
Answer: A function of fruit is it stores food materials which are used by animals as a source of food energy.
(1) Fruit protects the seeds from unfavorable environmental conditions and animals.
(2) In most cases, fruit helps in dispersal of seeds.
(3) Fruit also provides nutrition to the developing embryo inside seeds.
(4) Fruit stores food materials which are used by animals as a source of food energy.
f. What is rhizome?
Answer: A rhizome is an underground part of the plant that runs horizontally and has the ability to produce root and shoot systems in plants.
Or,
Rhizomes are networks of plant roots known as 'creeping rootstock' that live under the surface of the ground.
g. Which part of a plant absorbs water and mineral from soil?
Answer: Root is the part of a plant that absorbs water and mineral from soil.
h. What is the function of lenticel?
Answer: The function of lenticel is it facilitate the gas exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor in plant bodies that produce secondary growth.
Or,
The function of lenticel is - Lenticels allow the exchange of gases between the outer atmosphere and the internal tissue of the stem.
6. Long answer type questions:
a. What are the functions of a flower?
Answer: The five functions of a flower are -
i) Flower protects the seeds.
ii) Flower attracts the pollinator (insect, birds, etc.)
iii) Flower helps the plant to bear fruits and seeds after reproduction.
iv) Give protection to reproductive organs like stamen and stigma.
v) Most of all flower provides food.
b. Describe the process of pollination and fertilization.
Answer:
Pollination - Pollination is a very important part of the life cycle of a flowering plant. Pollination is the process of transferring pollen grains from an anther to stigma in a same flower or another. Pollen can be transferred by insects, birds, animals, winds, water, etc. Male gametes are found inside pollen and female gametes are found in ovules of a flower. Fertilization occurs only after pollination.
Fertilization - Fertilization occurs after the pollination of a carpel. After pollen landed to the stigma by the means such as insects, birds, animals, winds, water, etc., it reaches to the ovary through the pollen tube. Pollen tube carries male gamete present in pollen and female gamete in an ovule. The two gametes combine/fuses, fertilized and form a new seed.
c. Define:
i) flowering plants
ii) unisexual flower
iii) bisexual flower
Answer:
i) Flowering plants - A plant that produces flowers, fruit, and seeds are called flowering plants.
ii) Unisexual flower - A flower that possesses either stamens or carpels but not both is called unisexual flower.
Or,
A flower having either androecium or gynoecium is called unisexual flower.
Or.
Unisexual flowers are the flowers that have either stamens or pistil.
iii) Bisexual flower - Flowers having both male and female reproductive organs are called bisexual flowers.
Or,
A flower having both androecium and gynoecium is called bisexual flower.
Or,
Bisexual flowers are those flowers which contain stamens or pistil.
d. Describe the structure of fruit.
Answer: The fruit is defined as a fertilized and ripened ovary. The fruit consist of three parts and they are 1) epicarp, 2) mesocarp and 3) endocarp. Epicarp is the outermost covering of the fruit. Epicarp's function is to protect the inner part of the fruit. Mesocarp is the middle part of fruit which is usually fleshy. Mesocarp is the edible part of fruit. Endocarp is the innermost part of the fruit that encloses the seeds. Endocarp's function is to give protection to the seeds.
e. Why the roots modified? Explain.
Answer: The modification of root helps the plant to store the food to survive under unfavorable condition. The food is stored in form of starch and water. The modified root provides function other than absorption and support. So, the roots are modified because of the different purposes like storage of food and water, reproduction, photosynthesis, respiration, support, reproduction, etc.
f. Write a short note on modification of leaves.
Answer: Leaves itself is a food factory of the plant. The leaves has its own functionality and it may be modified into different shapes. Leaves may changed into tendrils to provide the support to the plants. Leaves are thick and fleshy to store water. Leaves may changed into thorns for protection and avoiding loss of water. Some leaves have unique modification which helps them to catch and digest insects.
g. For what purpose do the parts of plants modify?
Answer: The purpose of the parts of the plants modify because of the followings:
i) To adapt to their surroundings and environmental conditions.
ii) To provide the support to the plants.
iii) To store water.
iv) To catch and digest insects.
v) To store food and water.
vi) For reproduction.
vii) For photosynthesis.
viii) For respiration.
ix) To absorb food materials from the body of other plants.
7. Diagrammatic questions:
a. Sketch a complete flower and label its basic parts.
Answer: Sketch of a flower labelling its basic parts.
b. Draw a leaf and label its parts.
Answer: A leaf and labeling its parts -
c. Answer the following questions on the basis of the given diagram.
i) What is shown in the diagram?Answer: Female parts of a flower 'Pistil' is shown in the diagram.
ii) Which parts of it form seed and fruit?
Answer: Ovule forms seed and Ovary forms fruit.
iii) At which part do pollen grains come after pollination?
Answer: Pollen grains come to stigma after pollination.
iv) What are A, B,C and D? Name them.
Answer:
A = Stigma
B = Style
C = Ovule
D = Ovary
d. Answer the following questions on the basis of the given diagram.
i) Identify the stems.Answer: P, Q and S are the stems.
ii) What are the advantages of the modification shown in Figure U?
Answer: The advantages of the modification shown in figure U are -
↺ It stores water.
↺ It can be edible as a vegetable.
iii) Which diagrams show modification for the storage of food?
Answer: P, Q, R and U show modification for the storage of food.
iv) Identify corm and rhizome among them.
Answer:
Corm - S and T.
Rhizome - P, Q, R and U.
e. Answer the following questions on the basis of the diagrams given below.
i) Which of them have lenticels?Answer: A, B and D have lenticels.
ii) Which of them store food and participate in vegetative reproduction?
Answer: A and D store food and participate in vegetative reproduction.
iii) Which part of them is the reproductive part?
Answer: B is the reproductive part.
iv) Differentiate C and D in two points.
Answer: The difference between C and D in two points are -
| C (Leaf) | D (Sweet Potato) |
|---|---|
| 1. C (Leaf) prepare foods for plant. | 1. D (Sweet Potato) store foods. |
| 2. C (Leaf) has stomata which helps in gaseous exchange. | 2. D (Sweet potato) has lenticels which helps in gaseous exchange. |
v) Which part of them can prepare food?
Answer: C can prepare food.
vi) Which part of them has stomata?
Answer: C has stomata.
3.2 Invertebrates.
Test Your Concept
1. Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Poriferon | euglena |
| Sucker | hookworm |
| Single foot | earthworm |
| Tube feet | sycon |
| Cuticle | sea urchin |
| Protozoan | slug |
| Setae | spider |
| Jointed legs | leech |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| Poriferon | sycon |
| Sucker | leech |
| Single foot | slug |
| Tube feet | sea urchin |
| Cuticle | hookworm |
| Protozoan | euglena |
| Setae | earthworm |
| Jointed legs | spider |
2. Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
a. Animals having a backbone in their body are vertebrates.
b. Hard covering of a snail is called shell.
c. The phylum of microorganisms is Protozoa.
d. The animals having cylindrical and unsegmented body are kept in the phylum Aschelminthes.
e. Arthropods have compound eyes.
f. Hydra has stinging cells to paralyze the prey.
3. Multiple choice questions (MCQs):
a. Which one of the following animals belongs to the phylum Arthropoda?
A) ant
B) snail
C) earthworm
D) octopus
Answer: A) ant
b. Which of the following is kept in the phylum Aschelminthes?
A) hookworm
B) tapeworm
C) earthworm
D) sandworm
Answer: A) hookworm
c) What is the locomotory organ of hydra called?
A) setae
B) tentacle
C) flagellum
D) cilia
Answer: B) tentacle
d) Which one of the following animals belongs to the phylum Mollusca?
A) octopus
B) sea lily
C) hydra
D) sea anemone
Answer: A) octopus
e) Which one has no tissue?
A) hydra
B) cray fish
C) jelly fish
D) spongilla
Answer: D) spongilla
4. Differentiate between:
a. invertebrate and vertebrate
Answer: The difference between invertebrate and vertebrate are -
| Invertebrate | Vertebrate |
|---|---|
| 1. Invertebrates/They do not have backbone in their body. | 1. Vertebrates/They have backbone in their body. |
| 2. Examples of Invertebrates - amoeba, leech, hydra, etc. | 2. Examples of Vertebrates - human, dog, snake, bat, etc. |
| 3. Invertebrates/They are divided into nine phylum. | 3. Vertebrates/They are divided into five classes. |
| 4. Invertebrates/They possess an exoskeleton. | 4. Vertebrates/They do not possess exoskeleton. |
| 5. Invertebrates/They have simple nervous system. | 5. Vertebrates/They have highly complex nervous system. |
| 6. 95% of animal species are invertebrates. | 6. 5% of animals species are vertebrates. |
b. Euglena and sponge
Answer: The difference between Euglena and Sponge are -
| Euglena | Sponge |
|---|---|
| 1. Euglena is a single celled animal. | 1. Sponge is a multicellular animal. |
| 2. Euglena lives in water or in wet soil. | 2. Sponge lives inside water. |
| 3. Euglena moves from one place to another by the help of flagellum. | 3. Sponge cannot move from one place to another. |
| 4. Euglena has no capacity of regeneration. | 4. Sponge has capacity of regeneration. |
| 5. Euglena is spindle shaped. | 5. Sponge is massive/irregular shape. |
| 6. Euglena has no pore as sponge in their body. | 6. Sponge has several pores in their body. |
c. arthropods and annelids
Answer: The differences between arthropods and annelids are -
| Arthropods | Annelids |
|---|---|
| 1. Arthropods do not contain fully-segmented body. | 1. Annelids consist of a fully segmented body. |
| 2. Animals with jointed legs are what they are called. | 2. They are known as segmented worms. |
| 3. Arthropods have a free-flowing circulatory system. | 3. Annelids' circulatory systems are closed. |
| 4. Arthropods consist of one heart. | 4. Annelids consist of several simple hearts. |
| 5. Arthropods respire through tracheal tubes. | 5. Annelids respire through the soft moist skin. |
| 6. Arthropods can be found everywhere on the earth. | 6. Annelids are mostly aquatic and some are terrestrial. |
| 7. Arthropods have appendages that are joined together. | 7. Annelids do not have appendages. |
d. Ascaris and earthworm
Answer: The differences between ascaris and earthworm are -
| Ascaris | Earthworm |
|---|---|
| 1. Ascaris has a cylindrical and unsegmented body. | 1. Earthworm has a cylindrical and segmented body. |
| 2. Ascaris lives in the intestine of vertebrates. | 2. Earthworm lives in the soil, in burying organic matter, etc. |
| 3. Ascaris belong to the phylum Aschelminthes. | 3. Earthworm belongs to the phylum Annelida. |
| 4. Ascaris is called a round worm. | 4. Earthworm is called a segmented worm. |
| 5. Ascaris grows up to four feet long. | 5. Earthworm grows up to eight feet long. |
| 6. Ascaris does not have a blood, blood vessel or a heart. | 6. Earthworm has a heart, blood vessels and blood. |
| 7. Ascaris lives about for a year. | 7. Earthworm lives for two to three years. |
| 8. Ascaris can causes diseases to animals and plants. | 8. Earthworm changes the physical structure of the soil. |
#Important 8 differences between Ascaris (Aschelminthes) and Earthworm (Annelida).
5. Give reasons:
a. Starfish is not found in Nepal.
#Starfish is not found in Nepal, why?
Answer: Starfish is not found in Nepal because they are found in marine water only and Nepal is landlocked country.
Or,
Starfish is not found in Nepal because it is only able to survive in seawater and there is no Sea in Nepal.
Or,
Starfish are salt-water fish, to survive they need to be kept at the same salinity of the water they were raised in. So, starfish are not found in Nepal.
b. An earthworm is not kept in the phylum aschelminthes.
#An earthworm is not kept in the phylum aschelminthes/nemathelminthes, why?
Answer: An earthworm is not kept in the phylum aschelminthes because it is a segmented worm not a round worm.
Or,
An earthworm is not kept in the phylum aschelminthes/nemathelminthes because it lives in the soil, in burying organic matter, etc but not in intestine of vertebrates.
Or,
An earthworm is a segmented worm having a heart, blood vessels and blood whereas phylum aschelminthes/nemathelminthes doesn't have a heart, blood vessels and blood. So, an earthworm is not kept in the phylum aschelminthes/nemathelminthes.
c. Arthropods are more developed than annelids.
#Arthropods are more developed than annelids, why?
Answer: Arthropods are more developed than annelids because they(Arthropods) have more complex segmented bodies covered in an exoskeleton that protects their organs and muscles. Most arthropods also have visible distinctions between their heads, bodies and legs; this is not the case for annelids.
Or,
Arthropods are more developed than annelids because they show a well developed tracheal system and the respiratory system is not dependent on the circulation system.
d. Most of the flatworms and roundworms have undeveloped digestive system.
#Most of the flatworms and roundworms have undeveloped digestive system, why?
Answer: Most of the flatworms and roundworms have undeveloped digestive system because they are internal parasites and they absorb foods, nutrients through their body surface which are already digested.
6. Short answer type questions:
a. Write any two examples of mollusca/molluscs.
Answer: The two examples of mollusca/molluscs are snail and octopus.
b. Define invertebrate.
Answer: Those animals which are simple and without a backbone in their body are called invertebrates.
c. Name the organ used by hydra to swim.
Answer: The names of organs used by hydra to swim are tentacles and basal disc.
d. Which phylum includes soft unsegmented animals?
Answer: The Phylum Mollusca includes soft unsegmented animals.
e. What are compound eyes?
Answer: Compound eyes are visual organs that have many points of view which makes them able to look at all the directions without turning their heads.
f. Name an animal that has osculum.
Answer: Spongilla is an animal that has osculum.
7. Long answer type questions:
a. Classify the following with a reason:
i) Paramecium
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Protozoa | Paramecium is a single celled animal. |
ii) earthworm
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Annelida | They have an elongated and segmented body. |
iii) housefly
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Arthropoda | They have paired jointed legs. |
iv) liver fluke
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Platyhelminthes | They have flat and soft body, also called flat worm. |
v) ascaris
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Nemathelminthes/Aschelminthes | They have a cylindrical and unsegmented body. |
vi) starfish
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Echinodermata | Their body is covered with spiny skin. |
vii) sponge
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Porifera | Their body contains many pores. |
viii) jellyfish
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Coelenterata | Their mouth is surrounded by tentacles which help them in locomotion. |
ix) mussel
Answer:
| Phylum | Reason |
|---|---|
| Mollusca | They have a soft and unsegmented body. |
b. Mention any three special features of each of the following>
i) Protozoa
Answer: The three special features of protozoa are -
- Protozoa/They are unicellular and microscopic animal.
- Protozoa/They are mostly found in wet soil, water and in animals body.
- Locomotion takes place by flagellum, cilia or pseudopodia.
ii) Porifera
Answer: The three special features of Porifera are -
- Porifera/They have small holes/pores in their bodies.
- Porifera/They live in sea water.
- Porifera/They are the first multicellular organisms.
iii) Coelentereta
Answer: The three special features of Coelenterata are -
- Coelenterata/They have hollow pipe like body.
- Coelenterata/Their mouth is surrounded by tentacles.
- Coelenterata/They have capacity of regeneration.
iv) Mollusca
Answer: The three special features of Mollusca are -
- Mollusca/They have a soft and unsegmented body.
- Mollusca/Their body is covered with a hard shell.
- Mollusca/They are found in water and live on land as well.
v) Nemathelminthes
Answer: The three special features of Nemathelminthes are -
- Nemathelminthes/They have cylindrical and unsegmented body.
- Nemathelminthes/They live in the intestine of vertebrates.
- Nemathelminthes/They can cause diseases to animals and plants.
vi) Echinodermata
Answer: The three special features of Echinodermata are -
- Echinodermata/Their body is covered with spiny skin.
- Echinodermata/They moved with the help of tube shaped feet.
- Echinodermata/They have very high tendency of regeneration.
8. Diagrammatic Questions:
a. Sketch a well-labelled diagram of:
i) Amoeba
Fig: A well labelled diagram of Amoeba.
ii) Hydra
Fig: A well labelled diagram of Hydra.
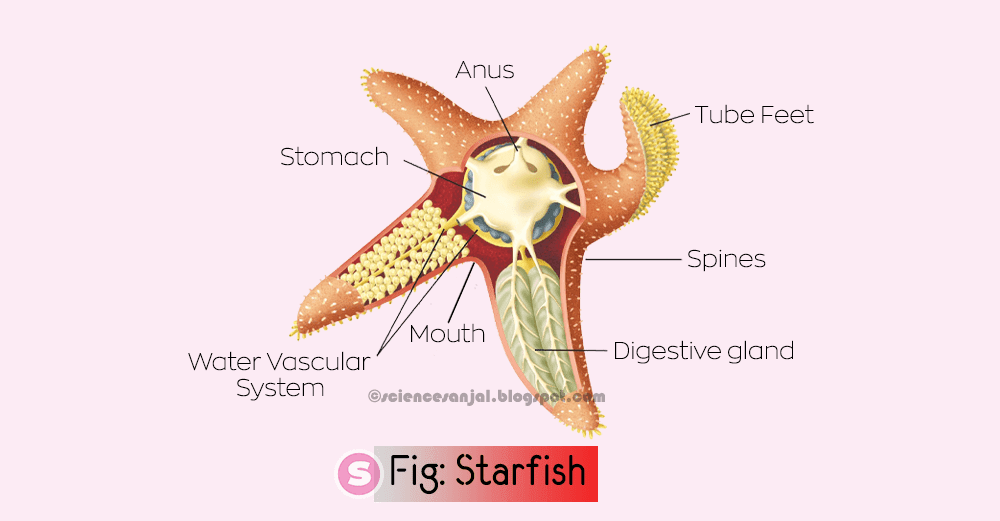
iii) Starfish
Fig: A well labelled diagram of Starfish.
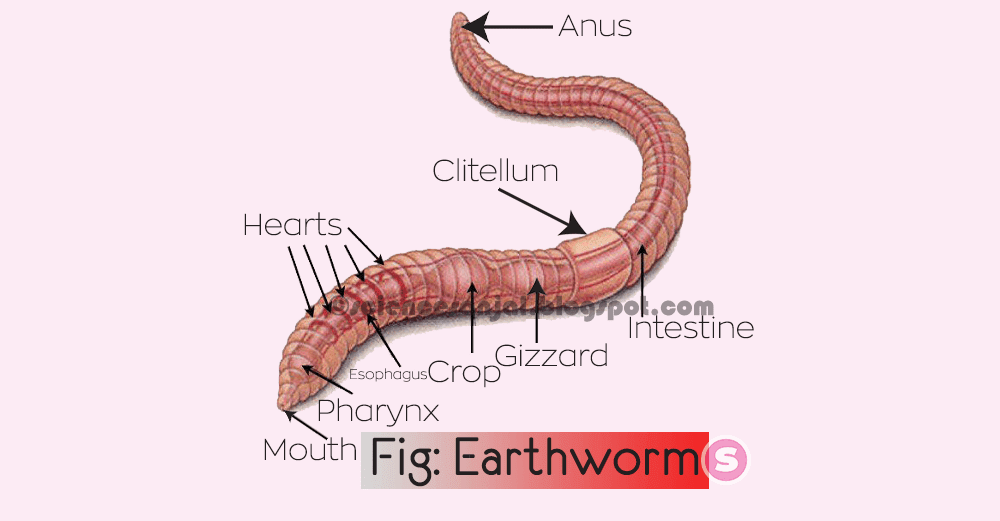
iv) Earthworm
Fig: A well labelled diagram of Earthworm.
v) Spider
Fig: A well labelled diagram of Spider.
b. Name the following animals and their related phylum. Answer the following questions based on the diagram.
Figure:
i.
Name - Snail
Phylum - Mollusca
ii.
Name - Starfish
Phylum - Echinodermata
iii.
Name - Hydra
Phylum - Coelenterata
iv.
Name - Liver fluke
Phylum - Platyhelminthes
v.
Name - Ascaris
Phylum - Nemathelminthes/Aschelminthes
vi.
Name - Housefly
Phylum - Arthropoda
vii.
Name - Paramecium
Phylum - Protozoa
i) Which animal has compound eyes?
Answer: Housefly has compound eyes.
ii) Identify the animal that has a single muscular foot.
Answer: Snail is the animal that has a single muscular foot.
iii) Which of them has cilia for locomotion?
Answer: Paramecium has cilia for locomotion.
iv) Which of them has a pipe like hollow body?
Answer: Hydra has a pipe like hollow body.
v) Which animal of them has its body covered with cuticles?
Answer: Ascaris has its body covered with cuticles.
vi) Identify the animals which are found:
- in ocean only.
- in the liver of animals.
Answer:
- Animal which is found in ocean only is Starfish.
- Animal which is found in the liver of animals is Liver fluke.
To be continued ... 😍
Check more -
Living Beings and Their Structure | Notes | Chapter 3 | Grade-7 | Science and Technology
#From above grade/class-7 science notes of Chapter-3 "Living Beings and Their Structure" New Course 2079-2081, we hope students will be able to:
- Describe the different parts of a flowering plant.
- Identify modified organs of plants (root, stem and leaf) and describe their structures and functions.
- Classify invertebrates and tell the characteristics of each group.
- Identify the components of animal and plant cells.
#Thanks for visiting us. We are really happy providing the notes of Grade/Class-7 Science, 'Living Beings and Their Structure' Notes based on new course of year 2079-2081 under Science and Technology. Please leave comments or suggestions so that we can improve.😊
[buttonLink style=unelevated elcreative_ripple]Search Terms:[/buttonLink]
[alert type=alert_outline]Grade 7 Science Notes of Chapter-3 Living Beings and Their Structure New Course 2079-2081., Class 7 Living Beings and Their Structure Science Notes., Living Beings and Their Structure Science Notes of Class 7., Check Notes of Living Beings and Their Structure Subject Science Grade/Class 7., Notes of Grade 7 Science Chapter-3 Living Beings and Their Structure New Course 2079-2081., Science New Course of Class 7 of year 2079., Class 7 Science 2079 New Course Notes-Solution., Class 7 Science Chapter-3 Living Beings and Their Structure Exercise Notes., Difference between pollination and fertilization class 7., Difference between stem and root grade-class 7., Difference between root system and shoot system class 7., Difference between stamen and pistil class 7., Functions of a flower, leaves, roots class 7., For what purpose do the parts of plants modify class 7., For what purpose do the parts of plants modify class 7., Class 7 chapter 3 Living Beings and Their Structures Question Answers.[/alert]










We welcome relevant and respectful comments. Off-topic comments and spamming links may be removed.
Please read our Comment Policy before commenting.